Autophagy, derived from the Greek words “auto” (self) and “phagy” (eating), literally means “self-eating.” Despite how it sounds, autophagy is not a harmful process but a crucial survival mechanism and a natural detoxification process for the body. It helps maintain cellular health, particularly under conditions of stress, by breaking down and recycling damaged or malfunctioning cellular components. This process is gaining considerable attention in the fields of aging, health, and disease prevention, as researchers continue to unravel its role in extending lifespan and promoting overall well-being.
This article delves into the science of autophagy, exploring how it works, why it’s important, its connection to longevity, and how lifestyle choices like fasting, exercise, and diet can stimulate this powerful cellular repair mechanism.
What is Autophagy?
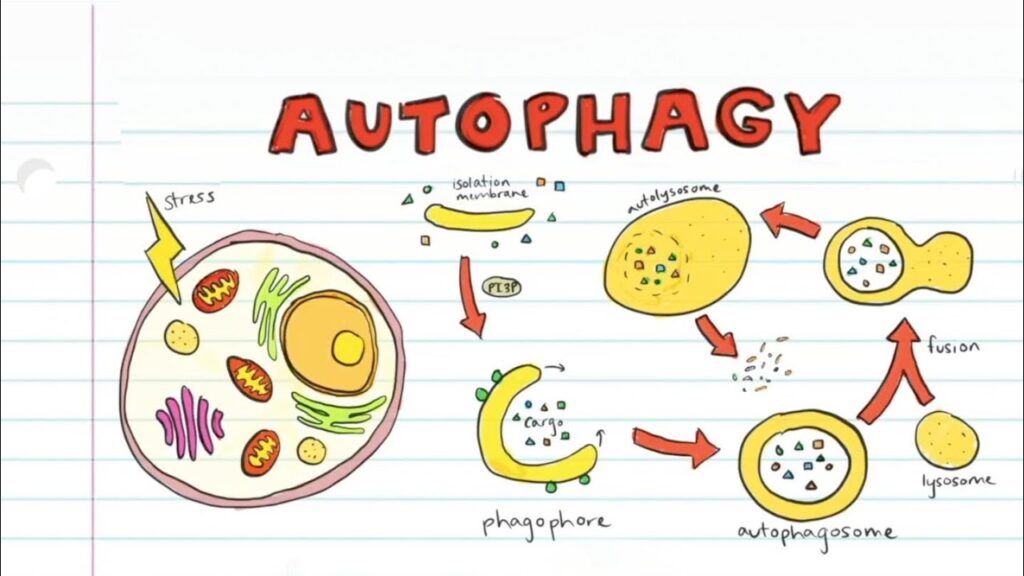
Autophagy is a highly regulated process by which cells degrade and recycle their own components. When a cell undergoes stress, either from nutrient deprivation, oxidative stress, or damage, it activates autophagy to maintain cellular integrity. The process involves the encapsulation of damaged or unnecessary cellular parts, including proteins, organelles, and pathogens, within a double-membrane vesicle known as an autophagosome. This autophagosome then fuses with a lysosome (a cell’s waste disposal unit) to break down the contents into usable molecules, which the cell can reuse for energy or to create new cell components.
In essence, autophagy is the body’s way of cleaning house, ensuring that cells remain healthy and free of toxic or dysfunctional parts that could lead to disease or aging.
The Autophagy Process: How It Works
Autophagy is a multi-step process involving several key stages:
- Initiation: Autophagy begins when the body experiences a trigger such as nutrient deprivation, energy stress, or cellular damage. Sensors in the cell, particularly mTOR (mammalian target of rapamycin), detect low nutrient or energy levels and initiate the process. When mTOR activity is inhibited (such as during fasting), autophagy is triggered.
- Formation of the Autophagosome: Once autophagy is initiated, a small structure called the phagophore forms. This phagophore surrounds the damaged or unnecessary cellular components, eventually becoming an enclosed vesicle known as an autophagosome.
- Fusion with Lysosome: The autophagosome then fuses with a lysosome, which contains powerful enzymes capable of breaking down the materials inside the autophagosome.
- Degradation and Recycling: Inside the fused autophagosome-lysosome complex, the enzymes break down the cellular debris into simpler molecules, like amino acids and fatty acids, which the cell can reuse for energy or to build new cellular components.
This continuous process of degradation and recycling is crucial for maintaining cellular homeostasis, particularly under conditions of stress or aging. It ensures that cells remain clean, functional, and free of harmful waste products.
Benefits of Autophagy
Autophagy offers a variety of benefits for both cellular health and overall well-being, many of which contribute to longevity and protection against age-related diseases. Here are the key benefits:
1. Cellular Cleanup and Repair
One of the main roles of autophagy is the removal of damaged or malfunctioning components within cells. This includes old, misfolded proteins that can aggregate and contribute to diseases like Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s. Autophagy helps maintain cellular function by clearing out this “junk,” allowing cells to operate more efficiently.
2. Promotes Longevity
Research shows that autophagy is strongly linked to increased lifespan and delayed aging. In studies on various organisms, from yeast to worms and mice, increased autophagy has been associated with longer life and greater resistance to age-related diseases. This may be due to autophagy’s ability to keep cells in a youthful, fully functional state by eliminating damaged parts.
3. Defense Against Disease
Autophagy plays a protective role in many diseases. For example, in the case of cancer, autophagy can prevent the initial formation of tumors by eliminating damaged cells before they become cancerous. However, in established cancers, autophagy can sometimes aid tumor survival, so the relationship between autophagy and cancer is complex. Beyond cancer, autophagy helps protect against neurodegenerative diseases, cardiovascular disease, and even infections by clearing out pathogens and toxins.
4. Boosts Immunity
Autophagy plays an essential role in the immune system by helping to eliminate invading pathogens, such as bacteria and viruses. By digesting these pathogens, autophagy helps prevent infections and supports the body’s natural defense system.
5. Energy Regulation and Metabolic Health
Autophagy ensures that cells can efficiently manage their energy resources, especially during times of stress. It helps cells recycle internal components into usable energy, promoting metabolic flexibility. This process is particularly important during fasting or periods of caloric restriction, as the body uses stored fats and proteins for energy. It also helps prevent obesity, insulin resistance, and metabolic disorders by ensuring cells stay metabolically healthy.
Autophagy and Longevity: Anti-Aging Potential
The link between autophagy and longevity has been the subject of extensive research, particularly in the context of caloric restriction and fasting, both of which are known to activate autophagy and extend lifespan in various organisms.
- Caloric Restriction (CR): Research has shown that limiting calorie intake without malnutrition can activate autophagy, reduce oxidative stress, and improve metabolic health. Caloric restriction is one of the most effective non-genetic interventions for extending lifespan across species. This may be because caloric restriction lowers insulin and mTOR levels, both of which are inhibitors of autophagy.
- Intermittent Fasting (IF): Intermittent fasting, where periods of eating are alternated with periods of fasting, is another powerful stimulator of autophagy. Studies suggest that fasting enhances autophagy, promotes cellular repair, and improves longevity by mimicking the effects of caloric restriction. Fasting for extended periods triggers the breakdown of old and damaged cellular components, leading to their replacement with new, healthy ones.
- Exercise and Autophagy: Physical exercise is another potent activator of autophagy. When you exercise, especially in the absence of food, your cells undergo mild stress, which stimulates autophagy. This helps remove damaged cellular components, boosts muscle repair, and improves metabolic health. Studies indicate that regular exercise can improve lifespan and reduce the risk of chronic diseases by enhancing autophagic activity.
- Sleep and Autophagy: Research also points to a strong link between sleep and autophagy. During sleep, the brain engages in its own form of autophagy, clearing out toxins and damaged cells to promote brain health. Chronic sleep deprivation, on the other hand, can impair autophagy, leading to the buildup of cellular debris and increased risk of neurodegenerative diseases.
How to Activate Autophagy Naturally
While autophagy is a natural process, there are several ways to enhance and activate it through lifestyle choices. Here are some of the most effective methods to boost autophagy:
1. Fasting
Fasting is one of the most powerful natural triggers of autophagy. When you fast, your body enters a state of nutrient deprivation, which activates autophagy as a survival mechanism. Studies suggest that autophagy is significantly upregulated after 16–24 hours of fasting, making intermittent fasting or extended fasts effective strategies for stimulating cellular repair.
2. Exercise
Both aerobic exercise (like running and cycling) and resistance training (like weightlifting) can increase autophagy. Exercise-induced autophagy helps your muscles repair and regenerate more efficiently while also improving metabolic health. Combining exercise with fasting can further amplify autophagic activity.
3. Caloric Restriction
Reducing your calorie intake without malnutrition can activate autophagy and extend lifespan. Caloric restriction mimics the effects of fasting, promoting cellular cleanup and improving overall metabolic health.
4. Nutritional Interventions
Certain dietary interventions can enhance autophagy. For example, ketogenic diets (high-fat, low-carb) have been shown to activate autophagy, as they mimic fasting by depleting glucose stores and forcing the body to burn fat for energy. Additionally, compounds like resveratrol, found in red wine and grapes, and curcumin, found in turmeric, have been shown to stimulate autophagy.
5. Heat Therapy (Saunas)
Heat exposure, such as through saunas or hot baths, can stimulate autophagy. Heat stress triggers cellular repair processes and enhances the removal of damaged proteins and organelles. Regular sauna use has been associated with reduced risks of heart disease, improved longevity, and increased autophagy.
Autophagy and Disease Prevention
Given its role in cellular repair and detoxification, autophagy has implications for a wide range of diseases. Here’s how autophagy impacts different conditions:
- Neurodegenerative Diseases: Autophagy is critical in clearing out misfolded proteins that can accumulate and cause neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s, and Huntington’s. Enhancing autophagy may help prevent or slow the progression of these conditions.
- Cancer: Autophagy can play both protective and harmful roles in cancer. In the early stages of cancer development, autophagy helps eliminate damaged cells and prevents tumor formation. However, in some advanced cancers, autophagy may help cancer cells survive under stress. Current research is exploring how autophagy modulation can be used in cancer treatment.
- Cardiovascular Disease: By clearing damaged mitochondria and reducing oxidative stress, autophagy helps protect against heart disease. Promoting autophagy through fasting and exercise may improve heart health and prevent cardiovascular events.
- Metabolic Disorders: Autophagy plays a role in regulating metabolism, particularly in clearing out dysfunctional mitochondria and reducing insulin resistance. Autophagy activation through fasting or caloric restriction may help prevent metabolic conditions like obesity and type 2 diabetes.
Conclusion: The Future of Autophagy Research
Autophagy is a powerful process that holds great potential for promoting health, longevity, and protection against disease. With ongoing research, scientists are exploring ways to harness autophagy for therapeutic purposes, including anti-aging treatments, cancer therapies, and strategies for combating neurodegenerative diseases.
Incorporating autophagy-stimulating practices into your lifestyle, such as intermittent fasting, regular exercise, caloric restriction, and heat therapy, can offer significant benefits for both health and longevity. As research continues to expand, autophagy may prove to be one of the most promising biological mechanisms for achieving a longer, healthier, and more resilient life